Deploying Django app to an AWS EC2 instance can be perceived as complex.
A lot of that complexity comes from the tricky process of creating an instance, access keys and not user friendly AWS interface.
This article will cover how to deploy your Django app to the AWS EC2 instance.
While AWS rightfully perceived as quite a tricky service to set up, if you follow this tutorial, you should have your app running on an EC2 instance in like 15 minutes.
If you are looking for tutorial for another cloud provider checkout out one of these:
- Deploy Django on Hetzner Cloud
- Deploy Django to Digital Ocean Droplet
- Deploy Django to AWS Lightsail
- Deploy Django on Linode
- Deploy Django on Azure
- Deploy Django to Google Cloud Platform
Table of contents¶
Django Application¶
The application used for this tutorial can be found here: https://github.com/appliku/djangotutorial
Your app should be pushed into a git repository. You can use GitHub, GitLab.
For ease of deployment we have the following recommendations:
- have the
requirements.txtfile in the root of your git repository. Don't forget to addgunicorn(or alternative) andpsycopg2-binary==2.9.5for Postgres support (orpsycopg[binary]) - Your app needs to respect environment variables like
DATABASE_URLfor the database credentials,ALLOWED_HOSTSfor the list of allowed domains,SECRET_KEYandREDIS_URLif applicable. - Please, don't forget to have DEBUG turned off when you deploy to a publicly accessible environment.
We have a full How to Start and Deploy a Django Project if you want to learn more
Also: check our SpeedPy.com SaaS boilerplate
AWS Account for Deploying to EC2¶
If you don't already have an AWS account, go to https://portal.aws.amazon.com/billing/signup to sign up.
Then go here to create a user that Appliku will use to perform server setup: https://console.aws.amazon.com/iam/home?#/users

Fill in the username, leave "Provide user access to the AWS Management Console" unchecked, click next.

On the next page switch to the tab "Attach Existing Policies Directly".
Add this policy:
AmazonEC2FullAccess
Then click the "next" button.
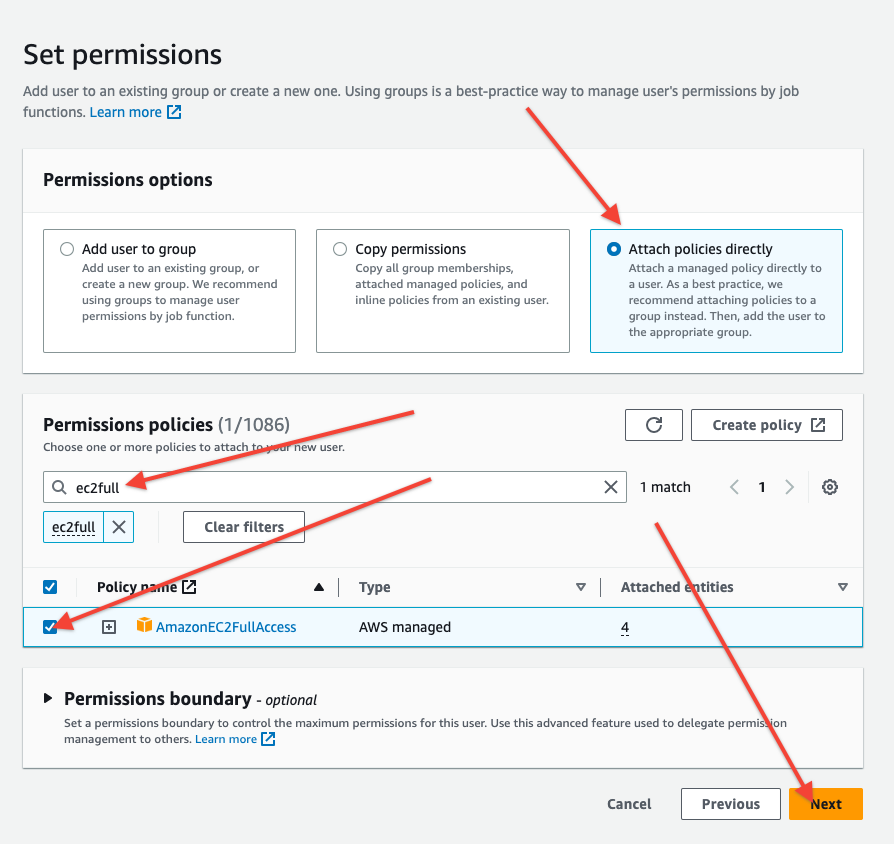
Click "Create user"

You will be taken to the list of users.
Click on the username of the newly created user.

Go to the tab "Security Credentials"

Click on the "Create Access Key" button.

Select "Thrid-party service", check the checkbox and click "Next", on the tag page leave it empty and click "Create Access Key"


Copy the credentials to the safe space!

Appliku Account¶
If you don't already have an Appliku Account create it by going here: Appliku Sign Up
Click on "Add a server"

Pick "Select Credentials" for AWS provider.

Paste your AWS access key and secret key and click "Test & Save Credentials"

If everything if fine, then "Status" must become active

Go to "Servers"

Then "Add Server"

You can now select the "AWS" provider

Select the region, instance type and the disk size. Keep in mind that to fit under the limits of free tier, the disk size must be under 30GB.
Click "Create EC2 Instance"

You will see the EC2 information page, which is empty for now. Appliku is waiting for AWS to provide us the server. This can take up to a minute.

After that Appliku will begin setting up the AWS EC2 instance for you installing all the required packages.
You can see that from the "Setup Status": "Started". You can also see the Setup Logs.

Server setup takes a few minutes. I recommend to stay here and wait until it finishes.
Sometimes cloud providers give a broken EC2 instance and setup fails. In this case you need to go to AWS console (the link "Manage Server in AWS Panel" will bring you straight to the needed page) and select the ec2 instance and terminate it. Then start the process of adding an EC2 instance once again.
Server setup is complete!

Creating and Deploying Django Application to EC2 Instance¶
Click on the "Applications" menu link

You will get to the Git Provider selection.

Creating application from GitHub¶
Select the "Setup Credentials" for GitHub.

You need to get a personal token from GitHub.
Go to this link to create a token: https://github.com/settings/tokens

Click on Generate new token -> Generate new token(Classic) Fill in the note, select expiration date, check the "repo" checkbox and "user:email"


And click "Generate token".
Copy the token from the next page.

Go back to Appliku dashboard and paste the GitHub Token, and click Test Credentials and Save

Status must change to "Active".
Click on the logo in top left corner to get back to your team and go to Applications again and create an app, select GitHub.

Fill the form with the app name, select the repository with your application, branch and select the server, click on "Create Application".

You will see your app has been created, but not yet deployed.

Creating application from GitLab¶
Alternatively if you use GitLab you should add credentials for GitLab and create an app from GitLab.
Go to Applications menu link, Click "Add Application" and Setup credentials for GitLab.

You need to create a Personal Access Token here: https://gitlab.com/-/profile/personal_access_tokens
Give the key a name, set or clear expiration date, select "api" checkbox and click "Create Personal Access token"

Copy the token and paste it in Appliku dashboard.
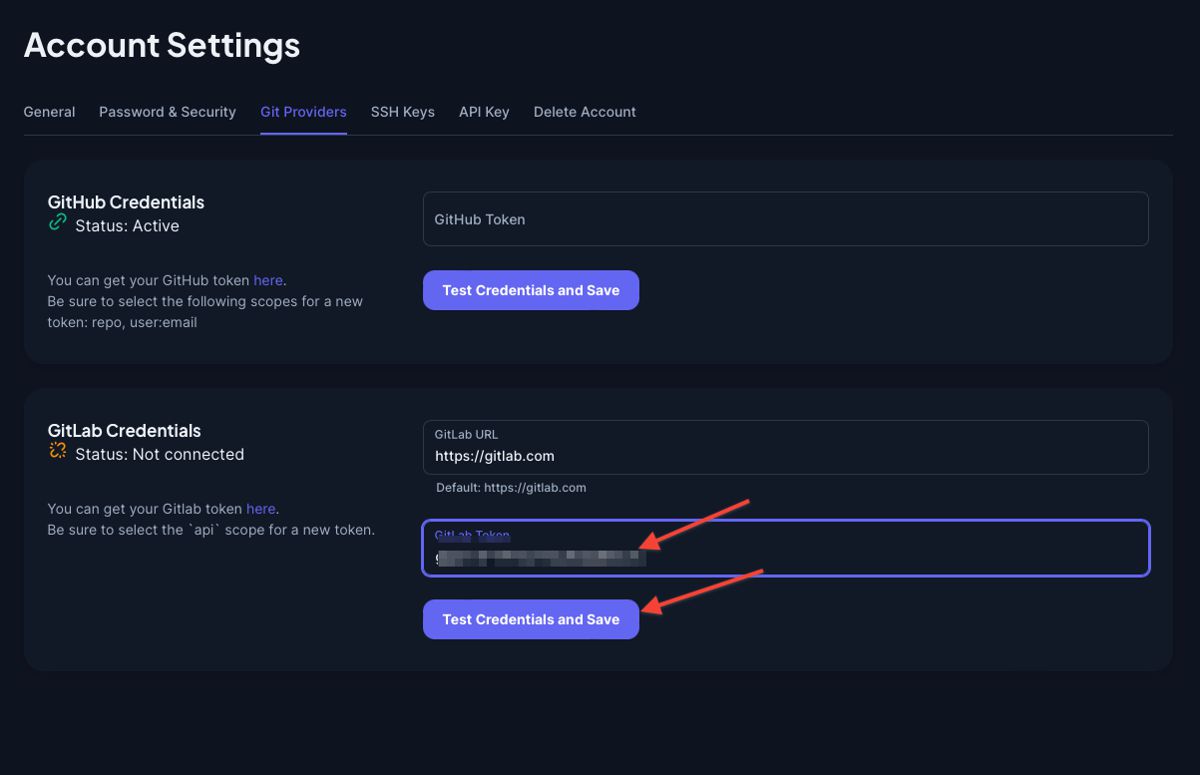
After you click "Test Credentials and Save" the Status should turn green and say "Active".
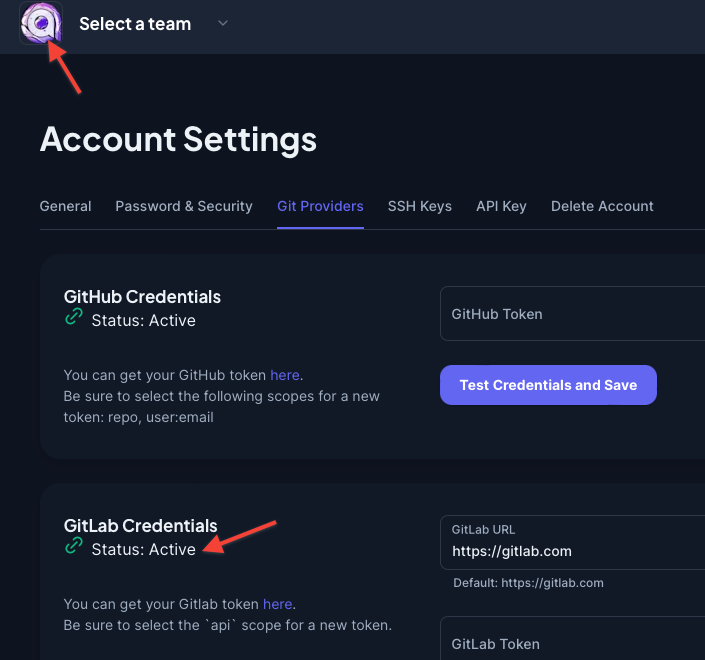
Click on the logo to go back to your team, go to Applications, Add Application and select GitLab

Give your application a name, pick repository and the branch, select the server and click "Create Application"

Setup the app¶
Databases¶
First, create a Postgres Database. Click on Add Database on the right

Select the Postgres 16 option and click "Create database"

Your database will start deploying, wait for the deployment status to become "deployed".

Define processes¶
Let's tell Appliku how to run your app
On the Application Overview page you will see a red triangle saying "No processes found".
Click on the "Add Processes" button.

Add two processes:
- one MUST be called
webto answer to HTTP requests and command should begunicorn project.wsgi --log-file -(pay attention to the last dash). It can be slightly different for your project - second one MUST be called
releaseand this is the command that will be executed after each successful deployment. If not specified it will default topython manage.py migrate. I recommend to create a bash script if your app needs to run several commands executed on each release. In our example, the command isbash release.sh
Click save and deploy button, a deployment will start.
Environment variables¶
Go to the "Environment Variables" tab and add env vars needed for your project.
At least specify the SECRET_KEY and ALLOWED_HOSTS.
These variables should be used by your app you can check here how to do that: https://github.com/appliku/djangotutorial/blob/master/project/settings.py
The SECRET_KEY variable value should be some long hard to guess string.

The ALLOWED_HOSTS variable should be a list of domains on which your app is accessible. As I already mentioned above, don't hardcode this, but make your app respect this environment variable.
By default, each app in Appliku receives a subdomain APPNAME.applikuapp.com, so in our example it should be mydjangoapp.applikuapp.com. If you add custom domains, make a comma-separated list like this mydjangoapp.applikuapp.com,example.com,www.example.com.
You can disable the default subdomain in build settings.
When you are finished with environment variables click the "Save and deploy" button and deployment will start.
Reviewing application logs¶
From the Application Overview page you can go to App Logs to check if there are any errors.


Open your application¶

To access your app click on "Open App" and click on the domain name. It will open your app in a new window.